While the Internet, Intranet, and Extranet are three terms we often hear in the digital space, they all have very different meanings. This article defines what they are, what the features are, gives examples, and has a comparison table to help you understand them definitively.
What is the Internet?
The Internet is an international network that links millions of devices and users. It is a public network that is accessible to anyone with a connection.
Features of Internet
- Open and accessible globally
- Source of unlimited information
- Used for communication, browsing, entertainment, and education
- Security depends on the user’s precautions (antivirus, VPNs, firewalls)
Example: Browsing Google, YouTube, or Facebook.
What is an Intranet?
An Intranet is a private network used only inside an organization. It is accessible only to employees or authorized users.
Features of Intranet
- Restricted access for employees
- Used for internal communication and collaboration
- Faster performance compared to the public internet
- Highly secure and managed by the organization
Example: A company’s HR portal or employee login system.
What is an Extranet?
An Extranet is an extended Intranet that gives limited access to external users such as partners, vendors, or clients.
Features of Extranet
- Controlled access for external stakeholders
- Useful for B2B communication and supply chain management
- Enables file sharing, order tracking, and collaboration with partners
- Requires strong security measures
Example: A manufacturer’s portal for distributors to view product catalogs and inventory.
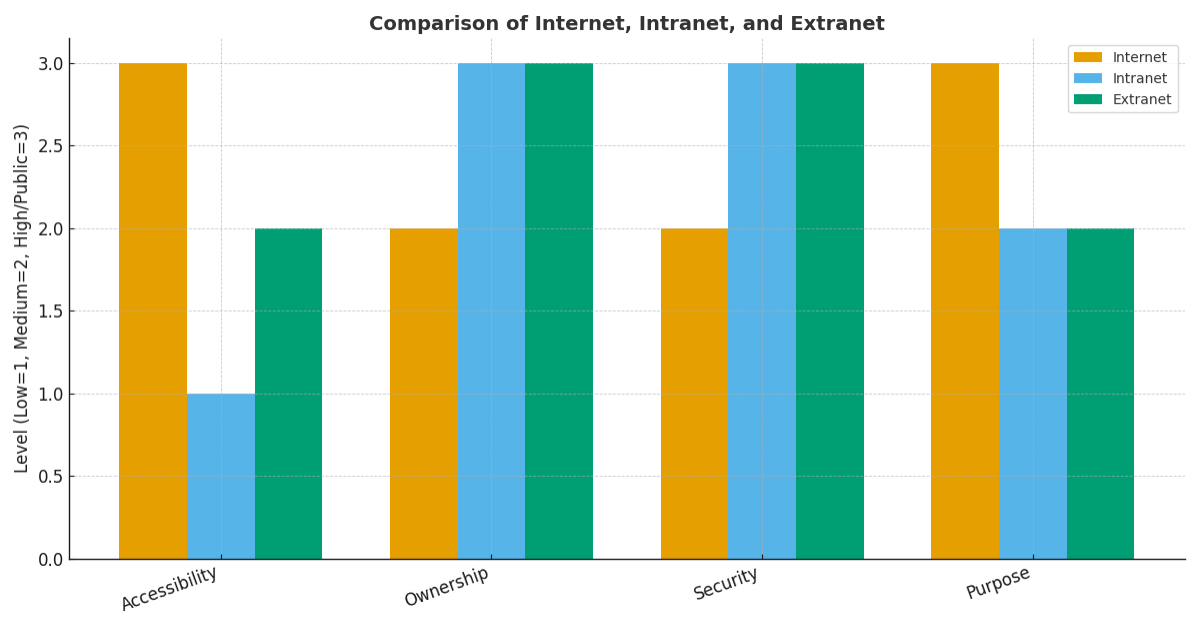
Internet vs Intranet vs Extranet
| Feature | Internet | Intranet | Extranet |
| Accessibility | Public, available to everyone | Private, only for employees | Semi-private, for trusted outsiders |
| Ownership | No single owner | Owned by an organization | Organization-owned, shared with partners |
| Security | Less secure, requires protection | Highly secure | Secure but needs strict control |
| Purpose | Global communication & knowledge sharing | Internal communication & collaboration | Business collaboration with external parties |
| Examples | Google, YouTube, Facebook | Employee portals, internal HR systems | Vendor portals, supplier dashboards |
Key Takeaways
- The Internet is public and accessible to all.
- The Intranet is private, designed for employees.
- The Extranet is semi-private, designed for business partners or clients.
👉 In short:
Internet = Everyone | Intranet = Employees | Extranet = Partners
FAQs
How does the Internet differ from an Intranet?
The Internet is available for anyone to access publicly, and the Intranet is privately used within an organization.
What is an example of an Extranet?
A Supplier Portal that provides business partners with access to track orders and share files.Which is more secure: Intranet or Internet?
Intranet is more secure when it is limited access and managed by the organization.